From Concept to Completion: 7 Integral Stages in Software Product Development for Project Onboarding
Everyone has ideas, but transforming them into successful, functional products or services is a formidable challenge. Indeed, it’s not an easy task. Innovation is key, but it must be paired with true value to make an impact.
According to research from the McKinsey Global Institute, out of every seven product ideas, only 1.5 actually launch, and a mere one achieves success. Furthermore, the failure rates for new products range from 25% to 45%. By adopting a systematic approach, you increase your chances of bypassing the common traps that lead to product failure.
New product requires investing time to thoroughly understand customer and market needs, stay ahead of competitors, and offer products that provide unmistakable value, thereby improving your chances of success.
Here is where the 7 Stages of Software Product Development become instrumental:

New Product Development (NPD) is a process used by companies to conceptualise, design, develop, and bring a new product to market. It’s a complex and multifaceted process that involves a combination of strategic planning, creative thinking, engineering, and market analysis. The goal is to create products that meet specific consumer needs or market niches while being economically viable and profitable for the company. Here’s a brief overview of what NPD entails:
- Idea Generation
The Idea Generation phase is the first and crucial stage in the New Product Development process. It involves brainstorming and creating a diverse pool of ideas for new products or enhancements to existing products. This phase sets the direction for the entire development process and is characterised by:
- Encouraging Creative Thinking: Fostering an environment where innovative and even unconventional ideas are welcomed.
- Diverse Sources of Ideas: Gathering ideas from various sources like employees, customers, market research, and technological advancements.
- Understanding Customer Needs and Market Trends: Conducting market research to align ideas with market demand and customer needs.
Emphasising on Customer Problems:
During this phase, a key focus is placed on identifying and understanding the problems faced by target audiences. This involves:
A) Personal Roadblocks: Understanding customer tendencies and prioritizing their primary problems. Using product design and development companies can help set the right tone before product development. Addressing the communication gap is crucial for productivity.
B) Qualifying Each of the Listed Problems: Employing a ‘4 U strategy’ to evaluate problems:
- Unworkable: Assessing if the product concepts will address real problems and achieve market fit.
- Unavoidable: Determining if the problem is inevitable and requires mandatory compliance.
- Urgent: Identifying if the problem is urgent and in high demand in the target market.
- Underserved: Looking for market whitespace where existing products don’t address user problems.
C) Emerging with Possible Solutions: Collaborating with a product development firm to produce feasible solutions for every identified user problem, thus creating new NPD opportunities.
D) Narrowing Down The Problems: Categorizing problems using a comparison chart with solutions and circulating findings within the organisation to finalise the viable problem set. Involving stakeholders in the process.
Approaches to Address Problems:
- Replicate: Creating a product similar to a competitor’s and launching it under new market conditions, focusing on unique features post-MVP launch.
- Re-Purpose: Rewiring an existing business model to present it more viably.
- Upgrading: Enhancing an existing model by addressing performance, speed, or adding functionalities to tackle competitors’ challenges.
This comprehensive approach ensures that the ideas generated are not only innovative but also deeply rooted in solving real customer problems, enhancing the likelihood of success in subsequent NPD stages.
- Idea Screening
The Idea Screening phase in the New Product Development (NPD) process is pivotal in selecting ideas with the highest potential for success. This stage involves a collective internal review of all generated ideas, seeking insights from individuals with industry knowledge and experience.
During this phase, it’s crucial to leverage tools like Proof of Concept (POC) to assess the feasibility of concepts. An idea that isn’t technically feasible to build should be discarded early in the process. Consulting with an Agile development team can provide valuable expertise in understanding the technical feasibility of ideas and aid in shortlisting those worthy of developing a POC.
In regions where software product development services offer cutting-edge technology solutions, the experience of smooth development is a significant advantage. This expertise plays a crucial role in the screening process, ensuring that only feasible and market-ready ideas proceed.
An essential practice during Idea Screening is conducting a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis. This analysis helps identify the opportunities and strengths of each idea, as well as potential threats and weaknesses. The process of conducting a SWOT analysis is relatively straightforward and can be initiated using a simple 2×2 grid.
Source Google
The Agile development team, including the product owner, scrum master, and product manager, engage in detailed analysis and shortlisting of ideas, weighing the opportunities and strengths against potential threats and weaknesses.
A successful New Product Development idea should ideally be unique and compelling enough to not require extensive convincing for people to pay for it. It should inherently address a specific need or gap in the market, making its value evident to the target audience.
In conclusion, the Idea Screening phase is about meticulously evaluating and narrowing down the ideas to those with the highest potential for market success, feasibility, and alignment with the company’s strategic goals.
- Concept Development and Testing
The Concept Development and Testing phase in New Product Development (NPD) is a multi-layered process that transforms selected product ideas into well-defined concepts and then puts these concepts through rigorous testing to ensure market viability.
During the Concept Development part of this phase, a company takes the promising ideas and develops them into concrete product concepts. This involves a detailed elaboration of what the product will be, its features, how it differs from existing products, and the benefits it will offer to the customer. Creating a prototype or a mock-up is crucial for tangible products, and for software or services, a detailed design or working model is developed.
This stage also requires collaboration across various departments. Teams from research and development, marketing, and finance work together to ensure the concept is realistic and feasible from both a technical and business perspective. The cost of development and launch is estimated, including production, marketing, and other expenses. Additionally, potential revenue from the product is forecasted, taking into account factors like market size, pricing strategy, and sales volume expectations. Ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations is also a critical part of this process.
Following concept development, the Concept Testing stage involves presenting the developed concept to the target market. This might include using surveys, focus groups, or individual interviews to gather customer feedback. The feedback is crucial as it provides insights into the acceptance of the product concept, highlighting appealing features and potential concerns.
Based on this feedback, the product concept is refined. This could mean altering certain features, changing the design, or even reconsidering the target market. In some cases, companies might conduct market testing by introducing the concept in a small, controlled segment of the market to gather more in-depth insights.
After analyzing the feedback and potentially modifying the concept, companies reassess its feasibility, both technically and economically. This reassessment ensures that the concept remains viable and aligns with the company’s resources and capabilities. The final step in this phase is a critical decision point: whether to proceed with the concept, make further adjustments, or discard it altogether.
Throughout this phase, thorough documentation of the process, feedback, cost estimates, and market testing results is maintained. This documentation aids in the transition to subsequent phases of NPD, such as detailed design and development, if the decision is made to proceed with the concept.
The Concept Development and Testing phase is pivotal in the NPD process. It ensures that the products pursued not only align with the company’s strategic and operational capabilities but also resonate with market needs and expectations, thereby enhancing the likelihood of the product’s success in the market.
- Market Strategy and Business Development
In the Market Strategy and Business Development phase of New Product Development (NPD), a comprehensive approach is undertaken to ensure the product’s successful entry into the market. This phase is about strategizing and planning how the product will be positioned, priced, promoted, and distributed to reach the target audience effectively.
Developing a Market Strategy
At this stage, the focus is on crafting a detailed market strategy. This begins with defining the target market by understanding potential customers’ needs, preferences, and buying behaviors. It’s essential to identify who the product is for and why they would need it.
The next step is product positioning. Here, the company decides how the product will be perceived in the market. This involves distinguishing the product from competitors and highlighting its unique value proposition. A well-defined positioning strategy clarifies why a customer should choose this product over others.
Pricing strategy plays a crucial role. The price must reflect the product’s value, align with market demand, consider production and operational costs, and take into account the competition’s pricing strategies. The right pricing can significantly influence the product’s acceptance in the market and its profitability.
Deciding on the most effective distribution channels is another critical component. Whether it’s online platforms, physical retail locations, or a combination of both, the channels chosen should align with where the target market is most likely to engage with and purchase the product.
A comprehensive promotional and marketing plan is then created. This plan should encompass strategies for advertising, public relations, digital marketing, and sales promotions, all aimed at generating awareness and stimulating demand for the product.
Conducting a Business Analysis
In parallel, a thorough business analysis is conducted. This includes forecasting the sales revenue, which considers factors like market size, product positioning, pricing, and chosen distribution channels.
Profitability analysis is another key aspect. This assessment evaluates whether the potential revenue from the product will outweigh the costs associated with producing, marketing, and distributing it.
The break-even analysis is vital for understanding the financial viability of the product. It helps determine the point at which revenue from the product will cover its associated costs, providing insight into the financial risks involved.
Assessing potential risks associated with launching the product is also crucial. The company needs to be aware of market uncertainties, competitive reactions, and any changes in customer preferences and be prepared with strategies to mitigate these risks.
Preparing for the Product Launch
As the market strategy and business analysis culminate, the company then moves towards aligning internal teams and preparing for the product launch. This includes ensuring that sales, marketing, and customer service teams are fully informed and trained on the product and its market strategy.
In some cases, test marketing might be conducted. This limited market launch provides valuable insights into the product’s performance and any adjustments needed before a full-scale launch.
Based on this feedback and the final business analyses, adjustments may be made to the product, marketing strategy, or other business plan elements.
Finally, the logistics of the product launch are planned. This includes deciding on the launch timing, preparing marketing campaigns, and coordinating with distribution channels for a synchronized and impactful product introduction to the market.
The Market Strategy and Business Development phase thus combines marketing acumen with business analytics to strategically introduce the product to the market, aiming for both reach and profitability.
- Product Design and Development
The Product Design and Development phase is a pivotal stage in New Software Product Development (NPD) where the conceptualized software idea begins to take a tangible form. This phase transforms the refined concept into a functional and market-ready product.
Embarking on Product Design
The journey begins with designing the software. This process involves creating detailed designs of the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX). Designers focus on making the software intuitive, user-friendly, and visually appealing. They incorporate elements like navigation, layout, graphics, and overall aesthetics to ensure the software is engaging and aligns with the target audience’s preferences.
Simultaneously, technical specifications are developed. These outline the software’s architecture, including the frameworks, platforms, and technologies to be used. It’s crucial that the technical design supports the software’s functionality and performance objectives while being scalable and maintainable.
Delving into Software Development
Once the design is finalized, the development team starts coding the software. This involves writing the code to bring the designs to life and implementing the functionalities as per the specifications. Developers work on different aspects like the front-end (user interface), back-end (server-side operations), and database management.
Throughout the development process, it’s important to maintain close collaboration between designers, developers, and the product management team. This collaboration ensures that the software aligns with the design vision and meets the defined requirements.
Iterative Development and Agile Methodologies
Many companies adopt agile methodologies for software development. This approach involves iterative development, where the software is developed in small increments, allowing for frequent feedback and adjustments. It provides flexibility and adaptability, ensuring that the software evolves as per the emerging needs and feedback.
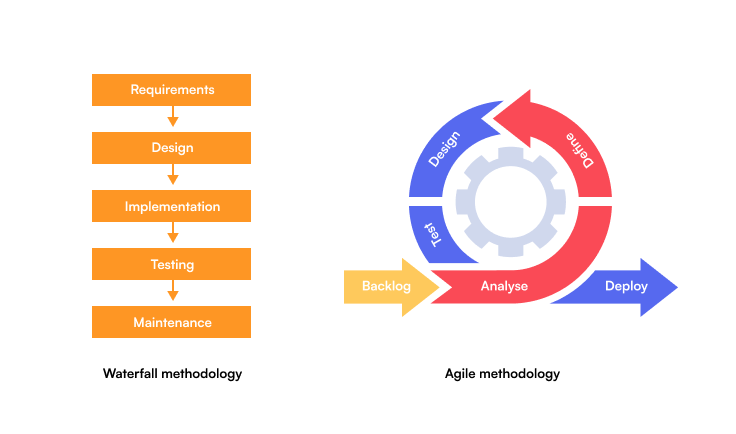
Source Google
Quality Assurance and Testing
Quality assurance is integral to this phase. The software undergoes various testing methods, such as unit testing, integration testing, and system testing, to identify and fix bugs. The objective is to ensure the software’s reliability, functionality, security, and compatibility across different platforms and devices.
User acceptance testing (UAT) is also conducted, where the software is tested in a real-world scenario by potential users. UAT helps in validating the software against user requirements and expectations.
Documentation and Compliance
Proper documentation of the software’s development process, its functionalities, and user manuals is crucial. This documentation assists in future maintenance and updates.
Additionally, ensuring the software complies with relevant industry standards and legal regulations is necessary, especially for software dealing with sensitive data or operating in regulated sectors.
Preparing for Deployment
As the software nears completion, preparations for deployment begin. This includes finalizing deployment strategies, setting up servers or cloud services, and planning for the distribution of the software.
The Product Design and Development phase is where the vision of the software product starts becoming a reality. It requires a harmonious blend of creativity in design, technical expertise in development, rigorous testing, and a keen focus on quality and compliance. This phase sets the foundation for a robust, user-centric, and market-ready software product.
- Market Testing
The Market Testing phase in New Software Product Development is an essential step where the software, almost ready for launch, is tested in a real market environment. This phase serves as a litmus test to gauge how the software will be received by its intended users and provides critical insights that can significantly influence the success of the product.
During this phase, the software is introduced to a selected segment of the target market. This controlled release can take the form of a beta version, a pilot program, or a limited rollout in a specific area. The key objective is to expose the software to actual users in a real-world scenario but on a smaller scale, allowing for manageable observation and analysis.
Feedback collection is a vital component of market testing. Direct input from users regarding the software’s functionality, user experience, and overall satisfaction is gathered. This feedback is crucial as it provides first-hand insights into the product’s strengths and areas for improvement, which might not have been previously identified during the development phase.
The company carefully monitors the software’s performance during this phase, analyzing user engagement, satisfaction levels, and any preliminary trends in usage or sales. This data is instrumental in making informed decisions regarding the full-scale launch of the software.
Market testing also allows for the fine-tuning of marketing strategies. Based on user feedback and market response, adjustments in the product’s marketing approach can be made, ensuring that the messaging, targeting, and promotional tactics are well-aligned with the market’s expectations.
Identifying and resolving any issues is another critical aspect of this phase. It’s an opportunity to address any bugs or usability concerns, ensuring that the product is as polished as possible before its full launch.
Based on the results of market testing, companies make crucial decisions regarding the future of the product. A positive response can green-light the product for a full-scale launch, while a lukewarm reception might lead to further refinement or even a reevaluation of the launch strategy.
Finally, documenting the findings and learnings from this phase is essential. This documentation not only serves as a guide for the current project but also becomes a valuable resource for future product development initiatives, offering insights into market dynamics and user preferences.
In summary, the Market Testing phase is more than just a trial run for the software; it’s a critical evaluation that tests the product’s market viability and guides the final steps before a full-scale launch.
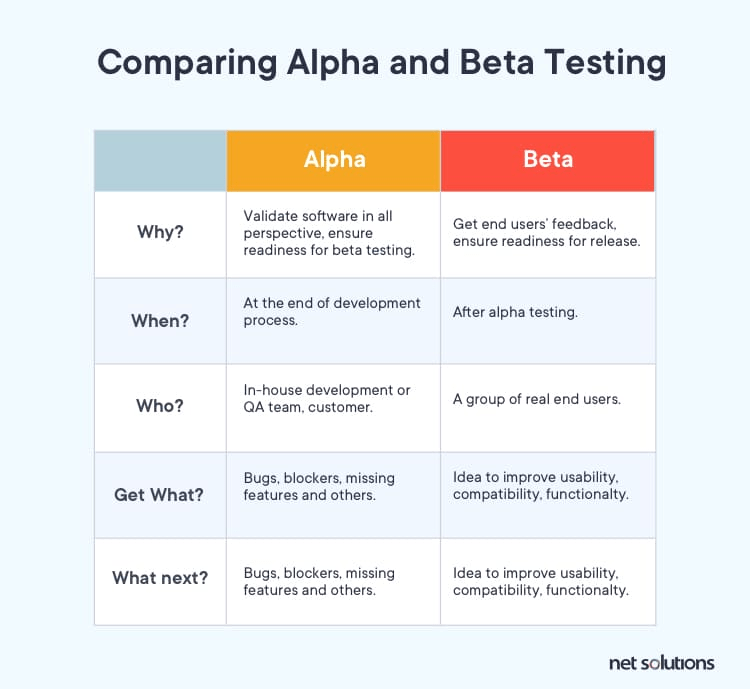
- Commercialization and Launch
The Commercialization and Launch phase in New Software Product Development (NPD) is the critical juncture where the software, having passed through development and testing, makes its debut in the market. This final phase is where the product’s success is truly tested, as it involves not just the release of the software but also ensuring its market penetration and acceptance.
As the launch phase approaches, the software undergoes final refinements. These adjustments are crucial, ensuring that any feedback from market testing is incorporated and that the software is polished, functional, and ready for public use.
A comprehensive launch strategy is essential for a successful introduction to the market. This strategy encompasses choosing an optimal launch date, coordinating various marketing activities, and preparing all promotional materials. The aim is to create a buzz around the product using a mix of marketing channels – social media, email campaigns, public relations efforts, and possibly events or webinars.
Ensuring the software is accessible to potential customers is a key focus. This means setting up effective distribution channels, which might include digital platforms like the company’s website, app stores, or cloud-based services. For B2B software, establishing strong partnerships for distribution can also be a significant step.
The alignment of sales and marketing efforts is vital. The sales team needs to be thoroughly briefed on the software’s features and benefits, equipped with sales materials, and prepared to handle customer inquiries and conversions.
Engaging with customers doesn’t stop at the launch. Collecting early feedback post-launch provides valuable insights into the software’s reception and highlights any urgent improvements needed. This ongoing engagement is crucial for refining the product and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Closely monitoring the software’s performance post-launch is important for understanding its impact and reception in the market. Tracking metrics like sales figures, customer feedback, and usage patterns helps in making informed decisions for future improvements.
Post-launch support and the release of updates are fundamental to maintaining the software’s relevance and addressing any emerging issues or user needs. Regular updates and responsive customer support contribute significantly to the long-term success and user retention of the software.
Finally, a thorough evaluation of the launch’s success is essential. This review covers the effectiveness of the marketing strategy, the sales performance, customer reception, and the extent to which the product met its initial objectives. The insights gained from this evaluation are invaluable for informing future product development and marketing strategies.
In summary, the Commercialization and Launch phase is much more than just releasing the software; it’s about ensuring that the product is strategically positioned for success, effectively marketed, readily available to the target audience, and supported post-launch for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, the journey from ideation to the successful launch of a product is complex and fraught with challenges. However, with a strategic and systematic approach, the odds of navigating these challenges successfully increase significantly. This approach involves a deep understanding of customer needs, market dynamics, and a relentless focus on delivering value that sets a product apart in a competitive landscape.
ABOVE Digital stands as a testament to transforming innovative ideas into successful realities. With our expertise in software product development, we guide ideas through the intricate process of becoming functional, market-ready products. Our team’s proficiency lies not just in technical execution but also ensuring that every product we develop truly resonates with its intended audience. At ABOVE Digital, we don’t just develop products; we materialise visions into tangible successes, setting the stage for our clients to lead and excel in their markets.
If you found our article interesting and gained new knowledge or useful information, don’t keep this knowledge to yourself. Share it in Social Media with your network to help others learn and be inspired. Spreading knowledge is a powerful way to connect and contribute to the continuous development and progress of our community.
Oto Peradze
CEO @ ABOVE Digital